Hey folks 👋
Welcome back to another SK NEXUS deep dive.
I’ve always loved learning new things, because I genuinely enjoy understanding how stuff works. But most of the internet doesn’t speak human anymore. Every article sounds like a PhD thesis, and that used to frustrate me.
That frustration is what brought me here - I couldn’t find simple explanations, so I started writing them for you.
Recently, I was working on a job case study where I had to write about quantum topics for a technical audience. I went in expecting it to be dull, It wasn’t. In fact, it pulled me in so deep that I ended up writing this - a version made for everyone, not just the experts.
So, let’s start from the ground up.
While we scroll through AI hype, a deeper revolution is already underway.
We got AI everywhere, in browsers, in short form, in my mom’s spaghetti. But the real underdog doesn’t live on your screen, it has been on a winter arc in the labs for decades.
“Amateurs seek the sun. Get eaten. Power stays hidden in the shadows” - Lewis Strauss
The ending of this quote reminds me about quantum technology and if you think about it…you will notice that’s exactly where quantum tech lives - in the shadows.
For decades, quantum sounded like something out of a sci-fi movie…but things have changed now.
The truth is - all of this started more than a century ago, when quantum mechanics was still an experiment in curiosity. That era is what we now call Quantum 1.0 aka the foundation of everything that followed.
What started in the early 1900s as pure theory, has evolved into a second revolution.
Now, we’ve stepped into Quantum 2.0 - an age where quantum computers aren’t lab toys anymore and where breakthroughs happen every other week.
Quantum 1.0 - The Beginning of It All
To understand where we are today, we need to rewind the clock.
Quantum computing didn’t just appear overnight, it’s built on over a century of discoveries in physics.
Before we could build quantum computers, we first had to realize that the universe itself doesn’t play by classical rules. That realization - that particles can exist in multiple states at once - is where it all began.
If you haven’t read The Evolution of Computers, I’d recommend checking it out - it’ll give you a strong baseline to connect the dots between classical and quantum worlds.
First, we would need to learn a bit of physics, but don’t worry, this isn’t a physics lecture - I’ll keep it simple, just enough physics to understand how we got here.
Setting the Stage
At the start of the 1900s, physics looked complete.
Newton had already explained planetary motion & gravity, Hooke had proven that light behaves like a wave.
At that time…to most scientists, the universe felt solved, but when researchers studied how light and heat behaved at microscopic scales, classical physics broke down and that’s when the cracks started showing.
Scientists were realizing that something fundamental is missing when they noticed that - hot metal didn’t glow the way the math predicted and Light acted like a wave one moment, and like a particle the next.
And that’s when a few rebels stepped up - Planck, Einstein, Schrödinger, and Heisenberg - each of them questioning what everyone thought they knew about reality.
Together, they uncovered the truth which had been hidden from a long time.
And it all began with Planck, the man who proved that even energy comes in tiny chunks.

The Birth of Quantum Theory (1900s-1930s)
Max Planck (1900): The Birth of the Quantum
Max Planck was a German theoretical physicist. He was the kind of guy who preferred math to drama….and just so you know - he wasn’t trying to start a revolution, he was just trying to fix an equation that didn’t make sense to him.
In 1900, he discovered that energy doesn’t flow like water; it moves in tiny packets, which he called quanta. That one idea flipped physics upside down - proving that energy is quantized, not continuous.
In short, Planck showed that nature runs on chunks, not streams.
Albert Einstein (1905): Light Comes in Packets
Albert Einstein - you already know the name, the E = mc² guy.
He took Planck’s idea further. While Planck applied quantization to heat, Einstein applied it to light. Years after Hooke showed that light behaves like a wave, Einstein took a deeper look and realized it wasn’t that simple.
Light, he proposed, acts as both a wave and a particle. Each packet of light carried energy - what he called a photon. This idea explained the mysterious photoelectric effect.
In short, Einstein proved that light isn’t just a wave - it can act as a wave, a particle, or even both at once, depending on the circumstances
Schrödinger (1926): The Equation That Changed Reality
Erwin Schrödinger was an Austrian physicist - the kind who turned deep questions into elegant equations. He was interested in math that could describe how the quantum world actually behaves.
He built a model called the wave function - instead of telling you exactly where a particle is, it tells you where it’s most likely to be. You can’t pin down its exact position, but you can predict the odds of finding it somewhere.
In short, Schrödinger showed that in the quantum world, certainty dies - everything is a matter of probabilities.
Heisenberg (1927): The Birth of Uncertainty
Werner Heisenberg was a German physicist and no this isn’t the guy from Breaking Bad. Basically, he was the type of guy who was unafraid to question the very idea of “knowing.” Instead of picturing what particles look like, he focused only on what could actually be measured.
That’s when he realized something wild - in the quantum world, the act of measuring itself changes what you’re trying to measure. You can know a particle’s position or its momentum, but never both at once. The more you know one, the less you know the other.
In short, Heisenberg proved that uncertainty is how nature actually works.
Tying the Threads
You’re probably wondering - Why did I tell you all this?
Because these were the puzzle pieces of the same picture.
Planck showed energy comes in chunks.
Einstein proved light can act like both waves and particles.
Schrödinger and Heisenberg built the math to describe it all.
Together, they laid the foundation of quantum mechanics…the science of how reality actually works.
The truth is - Quantum computing is literally the practical engineering of these same principles. Whatever term that you might have heard in the world of quantum computing - qubit, entanglement…etc all of them trace straight back to these early 1900s breakthroughs.
Now, that you have a general understanding of these concepts, you are on a solid path to understanding quantum computing not just memorizing cool tricks without knowing why they work.
And that’s the difference between a script kiddie of quantum hype and an actual quantum thinker.
When Theory Became Tech
Once the equations were cracked, it was time to test reality.
Scientists did what scientists do best - they started turning theory into tools.
Because, as Oppenheimer once said, “Theory will only take you so far.”
And so began the first quantum revolution - the era where physics met hardware:
Transistor (1947) - The first real proof that controlling electrons could control information. Without it, no phones, no laptops, no internet.
Laser (1960) - Einstein’s photon theory turned into beams so precise they could cut steel or perform eye surgery - revolutionializing medicine industry.
Semiconductors (1950s - present) - Quantum behavior of electrons in silicon made chips, microprocessors, and integrated circuits possible.
MRI (1970s) - Medical miracle powered by quantum spin. You don’t see atoms, but quantum mechanics lets you map them.
In short, the world quietly shifted - Quantum mechanics moved from chalkboards to factories, labs, and hospitals and just like that - what started as pure theory became the foundation of modern technology.
Quantum 2.0 - Where it started taking off
Welcome to Quantum 2.0 - the era we’re living in right now.
The age where theory turned into computation, and quantum finally meant hardware, not just equations.
But how did it all start?
To answer that, we’ve got to time-travel one last time - back to the 1980s.
Don’t worry, I’m not dragging you through more dusty physics; just one final leap through time before we hit the fun part.
The Birth of Quantum Computing (1980-Present)
The Founding Era (1982-1999)
In 1982: Richard Feynman lit the fuse. He asked a simple question: “Why not build computers that work the same way the universe does?”
In 1985: Just three years later, David Deutsch took that spark and turned it into theory. He described a universal quantum computer - a machine capable of running any computation, just like a classical one, but powered by quantum rules.
Fast forward to the 1990s - things started getting serious.
In 1994: Peter Shor introduced an algorithm that could break modern encryption by factoring huge numbers exponentially faster than classical computers - it’s famously known as Shor’s algorithm.
In 1996: Lov Grover followed up with a faster search algorithm, showing that quantum computers could outperform classical ones even beyond cryptography - it’s famously known as Grover’s algorithm.
By 1999, D-Wave Systems was founded - the first company openly dedicated to building a quantum computer.
By the end of the millennium, the idea had gone from physics lecture to engineering labs - and the quantum race had begun.
The Expansion Era (2000-Present)
In 2000: Edward Farhi and his team at MIT proposed adiabatic quantum computing.
By 2001: IBM and Stanford turned theory into reality, using a 7-qubit processor to run Shor’s algorithm. For the first time - they successfully demonstrated true quantum computation.

By 2010: D-Wave Systems released D-Wave One, calling it the first commercial quantum computer. Though limited, it proved that quantum hardware could leave theory behind.
In 2016: IBM opened its Quantum Experience to the public. For the first time, quantum computing was accessible - not just to scientists, but to anyone with an internet connection.
And in 2019: Google’s Sycamore processor achieved what was once thought impossible - quantum supremacy. It marked the moment quantum computing officially outpaced classical logic.
That was the short version of how quantum computing went from idea to impact.
The story’s far from over - new discoveries are happening almost every day, reshaping what’s possible. But before we dive into the latest breakthroughs, there’s one final piece we need to cover.
And also just for your understanding - following is a rough outline of everything so far.
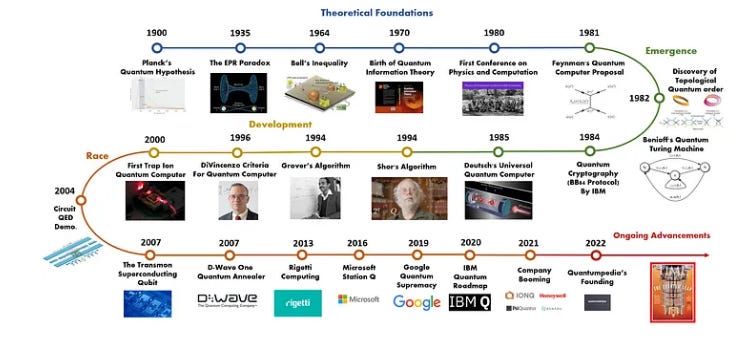
Quantum Basics - The Core Concepts You Must Know
So, you’ve made it through the history - congrats.
Now comes the real fun part: the fundamentals.
These are the core principles - the stuff you need to know if you want to sound like the cool guy who actually gets how this works.
Bit vs Qubit - The Core Difference
A bit (short for binary digit) is the smallest unit of information in classical computing.
It can only exist in one of two states - 0 or 1.
You can think of it like a light switch - it’s either off (0) or on (1).
Every program is built from billions of these bits flipping between 0 and 1
Bits are simple but they are also…limited.
On the other hand, a qubit (short for quantum bit) is the quantum version of a bit.
But unlike a classical bit, a qubit can be 0 and 1 at the same time - a state called superposition.
Think of it like a spinning coin - while it’s spinning, it’s both heads and tails. Only when it lands (when you measure it) does it become one or the other.
This “in-between” state allows quantum computers to process many possibilities at once. That’s why a few qubits can outperform millions of classical bits.
Once again - since tables help me see the difference, I made one for you as well:
Coherence - The Lifeline of Quantum Computing
Earlier, I talked about superposition - that it is the qubit’s superpower…but what I didn’t mention is that - it’s also its greatest weakness.
Qubits can, in theory exist as both 0 and 1 at the same time, but that state is ridiculously fragile. A tiny bit of heat or even a whisper of noise can knock a qubit out of superposition and force it to “collapse” into a definite 0 or 1.
All these effects break what’s called quantum coherence - the ability of a qubit to maintain its quantum state over time. When coherence is lost, we call it decoherence, and it’s the biggest villain in quantum computing.
Keeping qubits coherent is like keeping a soap bubble from popping in a hurricane.
Scientists are trying to fight it using different methodologies such as quantum error correction…etc. Don’t worry, we won’t being going deep into that (unless you enjoy brain pain), but just know this:
Coherence is everything.
Without it, quantum computing simply doesn’t work.
Entanglement - The Quantum Web That Binds Everything
Entanglement is one of the strangest and most powerful ideas in quantum physics. It happens when two particles - say photons or electrons - become linked in such a way that their states are no longer independent.
You can think of entanglement as - that if you touch one particle, then the other will feel it instantly. Einstein famously called it spooky action at a distance.
So, when you hear “entanglement” in the world of quantum computing - just know that it means - when two or more qubits share a single connected state. They act as one unified system, no matter the distance between them.
This instant correlation is what gives quantum computers their real superpower - the ability to perform multiple complex operations at once, a kind of shared brainpower classical bits could never achieve.
The Breakthroughs - How the Tech Is Evolving
Every other day, something big happens in the world of quantum technology and I am going to admit it, it’s quite hard to keep up with AI & quantum world news.
And now that you’ve got the fundamentals - it’s time to dive into some of the most recent quantum-breakthroughs redefining what computation even means.
Harvard’s Self-Healing Quantum Computer
Harvard just pulled off one of the most impressive experiments ever - a self-healing quantum computer. In simple terms, it can automatically detect and fix its own errors while running and this is a major step toward making quantum machines stable and scalable.
In the quantum world, two problems haunt researchers:
Decoherence
Atomic loss
We have already discussed decoherence, but atomic loss is also another major issue - it’s a headache unique to neutral-atom systems. Here, each atom represents one qubit, and sometimes those atoms just vanish from the grid. Other systems can reset qubits; this one loses them entirely.
Imagine a piano losing random keys mid-performance - that’s what physicists have been dealing with.
Harvard’s team partially solved this problem using different methods, basically they built a system that can detect when an atom disappears and instantly replace it - all while keeping the rest of the machine stable.
The result involved a quantum computer that can run for hours instead of seconds which is a very big thing in the world of quantum computing.
If you want to dive into the technical details of this particular breakthrough then you can visit my personal blog site for that.

Google’s Quantum Leap Beyond Supercomputers
Similarly Google also dropped another bomb in the quantum race - claiming its latest quantum computer has officially outperformed classical supercomputers.
In a recent experiment, Google’s team ran an algorithm that computed the structure of a molecule - a task so complex that even the most powerful supercomputers couldn’t handle it. It marks the first verifiable instance of a quantum system running an algorithm beyond classical reach, a milestone Google calls “repeatable, beyond-classical computation.”
What makes this matter? It’s a signal that quantum computing is getting closer to practical use in all the industries though Google does admit real-world applications are still years away.
But for now, we can say that - these machines can actually do something more than just theoretical benchmarks.
IonQ’s 99.99% Quantum Precision
We also have IonQ - which recently hit a new quantum milestone, its system can now perform one of the most fundamental operations, a two-qubit gate, with 99.99% accuracy.
But, wait…what the hell is a two-qubit gate?
In classical computers, logic gates like AND or OR take two bits and combine them. Quantum gates do the same with qubits, except they can entangle them - this connection, called entanglement, is what gives quantum computers their insane potential.
Single-qubit gate = changes one qubit’s state.
Two-qubit gate = links two qubits together.
You can think of it like this - Imagine a musician playing solo (a single qubit) vs a full band playing in sync (two-qubit entanglement). That harmony is where quantum power lives.
This matters because - this milestone means IonQ’s hardware can entangle qubits almost flawlessly which is indeed a step in the right direction.
The Global Push
While these headline breakthroughs steal attention, they’re just part of a much wider race. All over the world, labs and tech giants are grinding toward the same goal - making quantum computing actually work
Google is pushing toward fault-tolerant qubits - the kind that keep running even when errors hit.
IonQ and Rigetti are scaling quantum hardware for cloud use, making quantum access easier and broader.
Microsoft is betting on topological qubits - a theoretical but promising way to build quantum systems that could be far more stable.
Different paths, same finish line: a world where quantum machines leave the lab and enters the reality.
Beyond the Breakthroughs
So, what you read is a very high-level overview of what’s happening in the quantum space. Even the breakthroughs…they were just a handful, off the top of my head and by the time you’re reading this, there’s a good chance something else has already dropped. That’s how fast quantum computing is evolving.
But they’re still just steps - pieces of a much bigger puzzle that’s far from solved.
You’ll see headlines claiming “quantum supremacy by 2028” or “commercial quantum in five years.” Ignore the countdowns. No one knows how long it’ll take, maybe five years, maybe fifteen or maybe some superhero level physics breakthrough happens tomorrow and resets the clock entirely.
Either way, celebrate the progress - but keep your feet on the ground. The hype is loud, the reality quieter and that’s where the real story is.
The Industrial & Governmental Push
You have already seen that quantum tech is becoming more than just theory & science, it’s becoming the means to power.
Big tech and startups are moving beyond theory. They are focusing on building software, hardware and entire ecosystems that are needed to make quantum computing usable at scale.
This is the commercialization phase - where ideas are turning into infrastructure.
And it’s not just Big tech. Governments are also watching & funding - because whoever controls quantum computing controls encryption, intelligence, and digital warfare.
Call it what it is: a new front in global dominance.
Anyway, let’s look at how all this is unfolding in real-time and what it really means.
The Quantum Race Is Already On
If you look closely, you will realize how high different companies have moved quantum computing up their priority list - the proof is everywhere:
IBM is building real machines you can access through the cloud. Their 1,121-qubit Condor chip and the open-source Qiskit toolkit are early signs of a quantum-as-a-service future.
Google’s track record speaks for itself: Sycamore proved quantum supremacy in 2019, after that Willow dropped & on top of that they published the 2025 RSA research-paper - all this points towards the same thing - Google is engineering the future.
Startups like IonQ, Rigetti, and PsiQuantum are the wildcards, each betting on different hardware approaches. Some are already public, meaning quantum tech has entered Wall Street.
Even the infrastructure is taking shape - AWS bracket and Azure Quantum are examples of quantum access through the cloud not being a dream anymore.
In short, the race has already started and whoever gets there first will own the future of computing.
Governments Enter the Quantum Arena
You thought the quantum race is just a battle of technological supremacy? Wrong! It’s also a battle of power and that’s why different governments are furiously fighting the battle:
In the U.S - the National Quantum Initiative bundles research funding through NIST, NSF and DOE, are aims to keep America ahead of China in quantum computing, networking and cryptography. It’s a strategic move to ensure the country doesn’t fall behind.
China is not sitting idle, here are some of its major accomplishments:
It launched the satellite Micius in 2016 - the world’s first quantum communication satellite.
Established intercontinental quantum key distribution using Micius, sending encryption keys between China and Austria across ~ 7,600 km.
Reported to have begun mass production of stealth detecting quantum radars aimed at detecting stealth aircraft.
In Europe, the Quantum Flagship commits around €1 billion over ten years to build Europe’s quantum industry and achieve tech independence.
Pakistan is exploring deals with China under CPEC to establish quantum research hubs - I live here and I think it’s a bold move. Quantum dreams are great, but maybe start with stable Wi-Fi.
And trust me this list is never ending, from what I have seen it’s pretty clear that the Governments are trying to ride the quantum wave and in some cases, even steer it.
The Quantum Security Shift
Guess, what the first thing that quantum would break? It’s math.
Right now, attackers are already preparing for that moment through a tactic called Harvest Now, Decrypt Later (HNDL). It’s exactly what it sounds like:
Hackers copy encrypted data.
Store it safely.
Wait until quantum computers can decrypt it.
By the time we notice, it’ll be too late.
The scary thing is - HNDL doesn’t make noise and nothing that looks wrong - until one day, the encryption we rely on (RSA, ECC) simply stops working.
And just so you know this isn’t an “if” anymore - it’s when. In 2025 Google published new research showing that breaking RSA-2048 encryption could require fewer than one million noisy qubits and could be done in under a week.
That’s why the world is moving toward Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) encryption designed to survive quantum attacks:
Apple’s PQ3 protocol is already live in iMessage.
NIST has finalized its PQC standards for global use.
Microsoft and Apple have announced PQC support in upcoming OS releases.
If you believe HNDL is just a Big Tech problem, think again. Banks, hospitals, anyone moving encrypted data is already in the crosshairs.
And if you’re one of those who say “I have nothing to hide” - you’re at risk as well.
Imagine a breach where all that encrypted data sits untouched for years. But once quantum decryption catches up, it all unlocks at once. Old chats, medical records, transaction logs - everything coming back at once.
When that happens, it won’t be Big Tech that suffers first - It’ll be you.
If you want to learn more about HNDL and understand the dangers of it, then you can check out this piece - The Quantum Threat is closer than you think.
The Race for Digital Dominance
Alright, I’ll admit - that was a lot to take in.
But beneath all the technical noise lies a simple truth:
Governments see quantum as the next nuclear moment.
Whoever gets there first, sets the rules of digital warfare.
Control over encryption, privacy, and secure communication is the new world currency.
Governments know it, corporations know it, everyone knows it.
Beyond Quantum Computing
In the world of quantum tech - Quantum computing gets the majority of the spotlight but the reality is a bit different - Quantum computing is just a small branch of the bigger quantum world - the same way cybersecurity is one branch of computer science.
It’s important, but it’s not the whole story.
Quantum technology is stretching far beyond computers, we’re seeing:
Quantum sensors - Sensors that navigate without GPS
Quantum networks - for secure communication that can’t be intercepted
Quantum clocks - for ultra-precise timekeeping in satellites and finance
Quantum materials - Materials that could reshape energy and superconductivity
It’s the same story we saw decades ago. Early computers were slow, rare, and locked away in labs. Today, everything runs on them. Give it time, and quantum will follow the same trajectory - From labs to daily life - From theory to infrastructure.
If you want to see how that computer boom unfolded, check out my article on The Evolution of Computers:
And if history really does repeat itself - then we already know where this road leads.
It all reminds me of the Netflix series “Dark”:
“Everything repeats itself again and again for all eternity, because none of us are prepared to let go.”
I’m not claiming to predict the future, but from how things are moving, it’s clear we’re heading in the right direction - fast. Every other day brings a new breakthrough, a fresh milestone.
The Bigger Question: Power, Trust, and Control
Great job making it here - you’ve basically time-traveled from the 1930s all the way into the quantum age. But before we wrap this up, let’s slow down a bit.
By now, you probably know that - Quantum isn’t some sort of magic, it’s math, physics, and an insane amount of engineering. And scaling it remains quite hard. Decoherence, stability, energy cost, error correction - all of these still haunt researchers. Even Harvard’s atomic loss fix only solved it partially.
I get it, we’re moving fast…but we still have a long & tough road ahead.
And let’s not ignore the quantum hype.
The media loves to sell revolutions before they exist. Every industry loves to shout “revolution!” before the tech even works - Quantum’s no exception.
Look at NEO the humanoid robot praised like a digital messiah, but under the hood, it’s still limited. The same goes for the gaming industry - promises first, reality later.
If you are interested in learning more about the hype pattern, then check out my following pieces:
Anyway, back to the topic.
Sorry - my mind slips sometimes.
There is a positive side too - every generation of computing looked impossible before it happened. So while quantum’s full potential is still locked behind a few technical nightmares, what’s happening right now is promising.
The future looks bright, no doubt…
…But behind every bright future lies a power struggle.Quantum revolution is going to be a whole redefinition of control and when it’s embedded deep inside communication networks, finance, and national defense, the real question won’t be how quantum works - it’ll be who owns it.
Because the one who owns it, will be the one with the most control.
Now It’s Your Turn
I’ve said enough, now it’s your time to speak.
Do you think the quantum race will actually make the world safer or just shift control to a new set of gatekeepers?
And if quantum becomes as common as computers, will ordinary people benefit, or just get monitored more efficiently?
Share what you think below.
If you want more content like this, hit subscribe and restack. I’m on a mission to help people see through the noise, and make them understand what’s going on behind the curtain.
But for this to reach more people, I need your support. Subscribes and restacks aren’t just numbers - they’re what keep this mission alive and spreading.














“On the other hand, a qubit (short for quantum bit) is the quantum version of a bit.
But unlike a classical bit, a qubit can be 0 and 1 at the same time - a state called superposition.”
As a geek for this field, I’ve watched so many documentaries on qubits and superposition. It still is so interesting to me.
Great post.
This was such a good read!
You made quantum tech feel exciting without oversimplifying it.