Everyone has heard the term Blockchain but has anyone actually considered finding out how things work underneath the hood of this technology?
Most people think blockchain is only about digital currencies, but there is much more to this technology than just this. This booming technology has been grabbing the attention of almost every person in tech, and everyone wants to start a career in either blockchain or blockchain security, but what exactly is this technology? Is it some kind of magic?
In our modern society, techs like Blockchain and AI always attract new people because they seem like golden opportunities. Such technologies are presented to the public in a glamorous way; because of this, everyone tends to jump in on this train labeled as "success" since everyone wants to be successful.
Recently, the Bybit hack caught massive attention from almost everyone; even people who weren’t that tech-savvy heard about this. This made people even more curious about what blockchain is. But as always, instead of understanding the technology first, many just rushed in.
The very first thing that you need to understand is that Blockchain isn’t just a buzzword. It’s a powerful technology with real-world applications. However, if you dive into it without having a baseline understanding, you will regret it sooner or later.
Worry not! I am here exactly for that purpose, my friend. Today, my goal is to talk about different things that every beginner should know when the topic is Blockchain. Things such as what in the world blockchain is. How it works. I will also be debunking some common myths related to it and much more. Anyway, enough talking, let's get to the serious part.
Why was the Blockchain Created?
The world we live in runs on centralized systems. Centralized systems are the types of systems in which a single authority or an entity has control over the data, decision-making, transaction details, and much more. Different Banks and big corporations run on centralized systems; However, a centralized system has some flaws, such as:
1. They control everything; you’re just a user in their system.
2. They charge you for access fees, delays, and middlemen.
3. They make the rules, and you play by them, or you don’t play at all.
But guess what? Someone who clearly didn’t want to play by the rules and had a problem with the system ended up creating an entirely unique system where no single entity or authority was in control. A system where trust isn’t only as strong as “trust me bro” but rather everything is verifiable. That system goes by the name Blockchain.
At first, the applications of blockchain were limited, but it didn’t stay like that for a long period of time. In the beginning, blockchain was mostly utilized in crypto, it gave people a new way to send money without feeling like someone is spying on them. But now? It’s evolving at a really fast pace. Businesses, governments, and entire industries are using them in many ways and still are finding more ways to use this technology.
Since we now know why this technology was created, we can move on to the part where we explore what exactly this magical technology is. So, let’s get to that.
What in the world is Blockchain?
Blockchain, blockchain, and blockchain, but what exactly is this? I think it’s a better approach to break these terms down and then understand them. The term Blockchain consists of two terms: block and chain. Let’s understand them one by one to fully grasp the concept of what this technology is.
What is the Block?
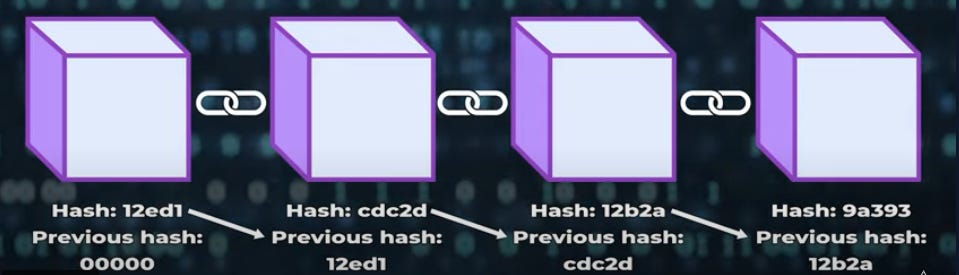
Think of a block as a digital record book. It stores multiple transactions, just like how the pages of a notebook can store different data. But this is where it gets interesting; the data stored in the blocks isn’t just plain data. It is encrypted, time-stamped, and sealed once the block is full. Why all this? So the data can stay safe, secure, and the integrity of data is maintained.
You might be wondering what kind of mysterious data this block is holding, right? Inside each block lies stuff such as:
1. Transaction Data: Details of what happened (who sent what, to whom, and how much).
2. A Unique Code (Hash): Think of it like a fingerprint for the block, ensuring its authenticity.
3. The Previous Block’s Hash: This is what links it to the last block, creating a secure chain.
Once a block is completed, it’s locked forever. No one can change its contents. The only way forward is by adding new blocks. But here’s where it gets interesting:
Recall that each block contains a unique hash. If someone even changes something as small as a single bit inside a block, the hash of the block changes instantly. And since every block is linked to the previous one through these hashes, a single change would break the entire chain, which is a literal massive red flag to the network.
Now, suppose you are a hacker and want to successfully change a past transaction, you would have to rewrite every block that came after it, across thousands of computers at once. And in a decentralized system, that is actually improbable - in theory, at least.
What is the Chain?
Now that we know what a block is, we can start understanding what a chain is because blockchain isn’t all about putting data inside blocks and gatekeeping it. It’s also about how these blocks are linked together to form a robust and unbreakable system - supposedly.
The block is the place or the container where transactions are stored, similar to how different data is written and stored in a notebook. But the chain is not about storing transactions or any kind of data. You can think of it as a literal chain, tying each block to the next one. At this point, you might be wondering why we even need this chain or what it even does. Well, from a high-level view, it performs the following jobs:
1. Responsible for linking the blocks: Every new block is connected to the previous one, ultimately making a chain of blocks.
2. Ensuring Security Through Hashes: Each block has a unique hash, and it also stores the previous block’s hash, making it nearly impossible for anyone to change the information inside those blocks. These hashes basically act as guardians for both the current block and the block before it. And this is all possible due to the chaining process of blockchain, mind-blowing, isn’t it?
How Does the Blockchain Work?
So, congratulations! If you have made it this far, it is because you now understand what the blockchain is and why it exists, but the most fascinating concept is still in the shadows.
Of course, I am talking about how it works. There are multiple steps to how a blockchain works, and I am going to make it all really simple for you. Anyway, enough of my yapping, and let’s actually get to the part for which we all have been waiting.
Step 1: Transactions are Created (data is recorded)
When I say “transaction”, it is not limited to money; transactions can include different things such as Supply Chain Data, Identity Verification, and much more. But, in order to keep things simple, we can simply use money as an example when talking about transactions. Imagine you’re sending money or signing a contract; each of these actions is a transaction. Guess what the cool part is? In blockchain, transactions are not stored in a central database like a bank’s system. Instead, they are stored in different blocks.
But here’s the thing: just because a transaction is created doesn’t mean it’s valid. Blockchain doesn’t blindly trust every transaction. Instead, every transaction needs to be verified before it’s added to a block, which is one of the main reasons why this technology is so secure.
Step 2: Transactions are Verified and Grouped into Blocks (Data is Bundled Together)
So, we have all these different kinds of transactions happening that include people sending and receiving data, money, or whatever the blockchain is being used for. But here’s the thing: they don’t just get added to the blockchain one by one because that is inefficient. Instead, what happens is that they are verified first for security purposes. After that, they are grouped into blocks. You can think of it as organizing different files into a folder before storing them away permanently. Makes so much more sense, right?
Once enough transactions have been collected and piled up, then we can move on to the next step. The next step is a security check that verifies whether the transactions are valid or not.
Step 3: Blocks are Verified Through a Consensus Mechanism (Security Check Before Entry).
Not everything gets a free pass onto the blockchain. Just like transactions were verified first and then grouped into blocks. Similarly, blocks are also verified first before a block is accepted into becoming a part of the blockchain. This is where the consensus mechanism comes in, kind of like a digital jury that decides if a block is legit or not.
Don’t get confused by the buzzword consensus; it simply means agreement from all parties, so in the context of blockchain security, you can think of it like every stage of security saying,
“All clear, the block is good, let it pass.” Until we have this call from all the stages, the block will not be added to the blockchain. Different blockchains have different ways of reaching consensus, but the goal is the same:
“To make sure every transaction is real and verified before adding it to the chain.”
These verification processes are crucial because these precautionary steps are the reason why blockchain is secure. You never know when a group of hackers might feel bored and plan to rip apart a technology. That is why it is essential to add such steps.
Step 4: Blocks are Added to the Chain (the Final Lock-in)
So, we’ve come a long way from home. Transactions were created, then they were verified, packed into blocks just like your dad (never) packs your lunchbox, and finally, those blocks went through another security check. Now what?
This is the final step, where blocks are literally locked in the chain, ultimately becoming a part of the family, i.e., blockchain. Once these blocks are added to the chain, they cannot be changed or tampered with.
Each new block is linked to the one before it, forming a chain, hence the term “blockchain”. And remember those hashes we previously talked about? They make sure that if anyone even tries to alter a single block, the whole chain breaks. This mechanism makes any kind of change nearly impossible.
Just like the American dad who never comes back home after going to get the milk, once a block is added to the chain, it never returns. It’s locked in forever, and it cannot be changed anymore. The only way forward is by adding new blocks.
Blockchain Uses Beyond Cryptocurrency
Whenever you mention blockchain, you might have noticed that everyone around you probably starts acting like they know everything about blockchain since they know 1 or 2 things about cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, Etherium, or maybe even some Sh1t coins. But here’s the thing: that’s just one piece of the puzzle. Blockchain isn’t just about digital money, it’s a technology with far bigger applications.
“Thinking blockchain is just for crypto is like thinking the internet is only for emails, completely missing the bigger picture."
I keep saying that there are many applications for this technology but haven’t mentioned them up until now, so let’s finally uncover this mystery.
Supply Chain Management
When you order your favorite coffee, have you ever thought about how many hands a product passes through before it reaches you? From factories to warehouses, they are then transported by different trucks. After that, they are handed to retailers. It’s a long journey. Along the way, things can get messy. Products get lost, swapped, or sometimes even falsely labeled, and other than that, generally so many bad things can happen, and it can be really hard to keep track of everything, right?
That’s where our boy blockchain steps in. Every time a product moves, a new entry is added to a shared, unchangeable ledger. This means that companies can track every step of the journey in real time. The problems that were faced previously aren’t an issue anymore. No more “lost” shipments, no more guessing if something is authentic or if it was swapped.
Big companies such as IBM are already using blockchain to make supply chains more transparent and trustworthy. So the next time you buy something labeled limited edition, blockchain might be the reason you can actually trust it.
Voting Systems
Ever wondered how safe the voting system is? In the past, many countries, including Pakistan, relied on traditional paper-based voting systems, and they still do. But a new system has also been on the rise for quite some time, aka voting using blockchain.
Different countries stick to the old method of voting because it is simple, and of course, it is easier to cheat as well; however, things won't stay like this for long because this revolutionary technology is here to change everything. Several countries have already implemented this technology in their voting system to enhance transparency and security.
Romania, Thailand, and Sierra Leone were the very first ones to adopt this system.
Ah, it seems so political, right? Let's cool it off a bit by discussing some working of this magic vote system. So, basically, when a vote is cast, it gets recorded in a block, just like any other transaction. Once it’s in, it’s locked in and cannot be changed. And recall from our previous discussion that once something the block becomes a part of a chain. There is no changing it.
While blockchain voting has been tested in some countries, its worldwide adoption might take a long time for different reasons. Many governments are exploring how blockchain can improve the voting system in different ways. But as I said earlier, switching from traditional voting methods to a blockchain-based system isn’t a piece of cake.
And honestly, there’s so much more to this topic than what I have covered here. If you’re interested in diving deeper and listening to me yap, drop a comment and let me know. I would love to hear your thoughts on this.
Real Estate & Land Registry
When it comes to buying property, the first thing that comes to everyone’s mind are thoughts like “we don't want to get scammed”, “we don't want to pay extra money to middlemen”, and so on. But guess what? No more worrying about getting scammed or getting shady deals because the Savior is here.
You might be wondering how blockchain is utilized at this point, right? Well, in a nutshell, once a property record is added to the blockchain, it cannot be altered without everyone knowing. So, if anyone tries anything, they get busted. On top of that, you literally don’t have to deal with those annoying middlemen who are trying to take their cut and leave you for dead because one of the sole reasons for the creation of blockchain was the elimination of middleman services.
Another major issue regarding lands also includes the following:
In Pakistan, land grabbing (qabza) is a big issue, it is because of corrupt record-keeping. Many people lose their properties because of fake documents, and sluggish legal processes, and on top of that there is bribery as well. Even if the courts favor the legal owner, things don’t go down the way they are supposed to. The illegal occupiers (qabzadar) simply refuse to leave.
Now, blockchain has the potential to solve this, it can gatekeep land records in a way no one can mess with. No more fake documents, just hard proof of who owns what. Blockchain doesn't care who you are. All it knows is that if it's not yours, you can’t take it.
Some countries are already experimenting with blockchain for land registries. For now, Sweden, Georgia, and Dubai are leading the way in creating a new world where the lesser evil exists by eliminating real estate fraud.
But, just like voting, full adoption takes time. There are tons of steps involved in making such a big change in the system. Governments need to update their legal systems and integrate blockchain, and who knows how long that will take. Until then, we’re stuck with the same old paperwork mess.
Further Applications
Blockchain is no longer just a buzzword in the world of digital currency. While we’ve covered some of its current applications, like supply chain management, voting systems, and real estate, these are only the beginning.
Companies are experimenting with blockchain for everything from tracking carbon footprints to streamlining government processes. As blockchain technology improves, we are likely to see even more use cases of this technology rise from the shadows. And, if you are curious to find even more applications of this technology, then I have to say that is where your personal research steps in.
I have merely shown you the path; now, it's your job to walk on it.
But What About Cryptocurrencies?
You caught me! My hands are up, sire! I hate to say it, but yes, cryptocurrencies are the most widely recognized and famous use of the magic technology called blockchain. Currencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and others have truly put blockchain on the map of this world.
These currencies are indeed the reasons why even an average Bashir from Karachi or Jimmy from New York knows about blockchain. But here's the thing: While crypto is the most famous application, it’s not the only one. (Never forget that.)
Indeed, blockchain has the potential to transform entire industries. But since crypto has been one of the main reasons for the rise of blockchain. Let’s dive in to understand how blockchain works in some famous digital currencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
How Bitcoin & Ethereum Use Blockchain
Bitcoin was the first-ever digital currency that showcased blockchain’s potential. Since you have already learned how blockchain works, things will be far easier to understand now. Both Ethereum and Bitcoin use blockchain, but they function a bit differently. Let's learn how they use blockchain and explore the major differences between them:
Step 1: A Transaction is Made
In Bitcoin: Someone sends BTC from one wallet to another.
In Ethereum: Someone sends ETH or interacts with a smart contract (like buying an NFT).
Step 2: The Network Receives the Transaction
The transaction gets shared with multiple computers (nodes) on the network.
After that, the computers check if the sender has enough funds and if the transaction is valid.
Step 3: Transactions are Grouped into a Block
Instead of adding transactions one by one, multiple transactions are gathered in one block.
This makes the process faster and more efficient.
Note: “Before you proceed to the next step, I highly suggest you understand what Proof of Work and Proof of Stake are. Since it is out of the scope of this article, I will not be explaining it.”
Step 4: The Block Gets Verified and then Gets Added to the Blockchain
Bitcoin: It uses Proof of Work (PoW); Miners compete to solve a puzzle, and whoever solves it first can add the block to the chain, and this process repeats roughly every 10 minutes.
Ethereum: It used to use PoW but now uses Proof of Stake (PoS). In PoS, there’s no competition. Instead, validators are randomly chosen based on how much ETH they stake, and they agree on a single block to add.
After the block has been verified, it simply becomes a part of the blockchain.
The core purpose of both Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) is to verify that the blocks are valid before adding them to the blockchain. Both methods ensure that only legitimate transactions get recorded and keep the blockchain secure. The only difference is how they choose who gets to validate the next block.
Step 5: The Transaction is Finalized
After all the previous steps, the transaction is finally permanently recorded.
In Bitcoin, this means that BTC was sent successfully.
In Ethereum, it could mean ETH was sent or a smart contract was executed.
Common Myths About Blockchain
Finally, the discussion for which we have all been waiting for decades. The mysterious myths of blockchain. Yeah, yeah, I get it, every kid you meet has his own theory of how not secure blockchain is or how blockchain works, and I'm also sick of it. So, why not bust open the brains of these myths, eh? Let’s do that with some of the most famous myths.
Myth #1: Blockchain is Not Secure
Reality: Actually, it’s one of the most secure technologies out there. Blockchain operates on a decentralized network, meaning no central authority controls it. On top of that, each piece of data is cryptographically (complex mathematical functions) protected, and recall that once something is added to the blockchain, it becomes history; you cannot change it.
Myth #2: Blockchain is Only For Crypto
Reality: Blockchain has a very wide range of applications, and it is not just for crypto. I have emphasized this very specific topic throughout the article, and the reason for that is that I need you to get this myth out of your brain and say goodbye to it. While I admit that cryptocurrency is the most famous use case of blockchain, it’s far from the only one.
Blockchain is being used in different industries, such as healthcare, supply chains, and even in voting systems to ensure tamper-proof elections. It’s basically becoming a backbone for many sectors, not just crypto.
Myth #3: Blockchain is Too Complicated
Reality: Well, if you've made it this far and understood everything up until now, I’m curious to know what you would say if someone asked you, “Are the basics of blockchain hard?”
Leave a comment below to answer that; I would love to hear what's going on in your mind.
Anyway, back to the topic, I know Blockchain may seem intimidating at first. When I had to research this topic, I was scared of it as well, but once you break the concepts down and understand them one by one, it’s actually quite simple.
And that is exactly how I wrote this piece- to make things easier for you. Sure, the tech behind it might sound complex, but the basic idea is super easy to grasp. In a nutshell, all that happens is the following:
-Transactions are recorded.
-Transactions are grouped into blocks.
-Those blocks are then added to a chain of records.
What Comes Next?
The truth is that blockchain is a recent technology, and it is only getting warmed up. The potential it has to completely change everything is off the charts. The old world was full of systems that move at the speed of a snail, middlemen that would put holes in your wallet, and companies that would rob you of your precious data. But that is slowly changing. As you read this, in the meantime, there are people out there burning the midnight oil to find ways through which they can implement this hot technology and make our lives more private, secure, and fair.
Web3 is knocking the doors down just like the FBI knocks open the doors of criminals, and that is not it. We also have the DApps. What in the world are these? Well, you can think of them as apps that don’t bow down to corporations or governments. No more “Sign in with Google” nonsense. Your data stays yours. You own what’s yours. And that changes everything.
Ah, yes, the good old Pakistan. You thought I forgot about my own country? I would like to, but I can't (xD). I don't know what will happen in the future, but I do know that if Pakistan plays its cards right, it could be next in line to build something that actually works. Just for a second, maybe forget crypto; “blockchain” could just flip the script on how tons of things run. You name it: Land records, digital identities, supply chains. And the thing is, many countries like Estonia are already in the game, so it's not like bringing this vision to reality is impossible.
So, the question is, when the world finally wakes up to blockchain’s full potential, which it will sooner or later, will you be ahead of the game or just another spectator?
The Bottom Line
We’re coming to the end of this journey, but blockchain’s story is just getting started. We talked about tons of stuff today. In the beginning, we didn’t even know what blockchain is or why it is even called blockchain, but you now know the basics of blockchain. Maybe you can flex that knowledge in front of your computer science teacher to make her fond of you (that is exactly what I do).
I get it; your mind is screaming with questions like “Is blockchain going to die?”, “Should we jump into this career?”. But this isn’t the first time a disruptive technology was introduced to the world and the world was left in question. Think about it: once upon a time, people doubted the Internet, too.
Look where we are now. Whether you’re a developer, an investor, or just someone keeping an eye on what’s next, one thing’s for sure, and what is that? Blockchain isn’t going anywhere.
Aside from all that, I believe one of the most important points we touched on today was that blockchain isn’t all about cryptocurrency. Whoever says that is clearly unaware of the bigger picture. Blockchain has such wide applications, and if you have made it this far, then you surely know what I am talking about. This technology is transforming industries beyond just digital currencies. From healthcare and voting systems to supply chains and real estate.
So whether you’re an individual trying to protect your data or someone eager to dive into the world of blockchain technology, there’s no denying that understanding how blockchain works and how it can be applied is a skill worth investing in. And, while this might be the end of this article, it’s just the beginning of your journey with blockchain. Keep learning, keep exploring, and most importantly, stay curious.
Apart from all our discussion, there is one important thing that I would like to cover. Any guesses on what that might be? Ground reality! Blockchain is a powerful tool, maybe too powerful. And while it promises control, decentralization, and security, there is one big question hanging over it:
Would governments really want to adopt this technology? Would they be willing enough to hand over control and let an average Bashir truly own his assets, his identity, his freedom? Probably not.
You see…power relies on control, and blockchain changes that. I am not saying that there is a problem with the tech itself, but the real fight isn’t about innovation, it is about who gets to control it. And unless the average Bashir becomes a tech wizard,
so that he can run his own network, governments won’t be handing over control…
at least not that easily.
Phew… We covered a lot of ground today, diving into both the potential and the reality of blockchain. But at the end of the day, if you want change, you’ll have to take things into your own hands.
Anyway, that being said, I’d love to hear your thoughts. Drop a comment below and let me know what you think. Your feedback helps me level up, and trust me, I love that.
Further Learning
Want to build something on your own?
Looking for people who get it, who are figuring things out just like you?
The Wandering Pro is a quiet corner of the internet where freelancers, tech workers, and first-time builders gather to make steady progress - one challenge, one win, one project at a time.
Join The Wandering Pro; find your rhythm, share progress, and grow with a community backed by decades of real-world building experience.








“cryptocurrencies are the most widely recognized and famous use of the magic technology called blockchain. Currencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and others have truly put blockchain on the map of this world.”
It’s true they are. Something about bitcoin caught the public’s imagination. But as you show in this post, blockchain is so much more!
Great read!